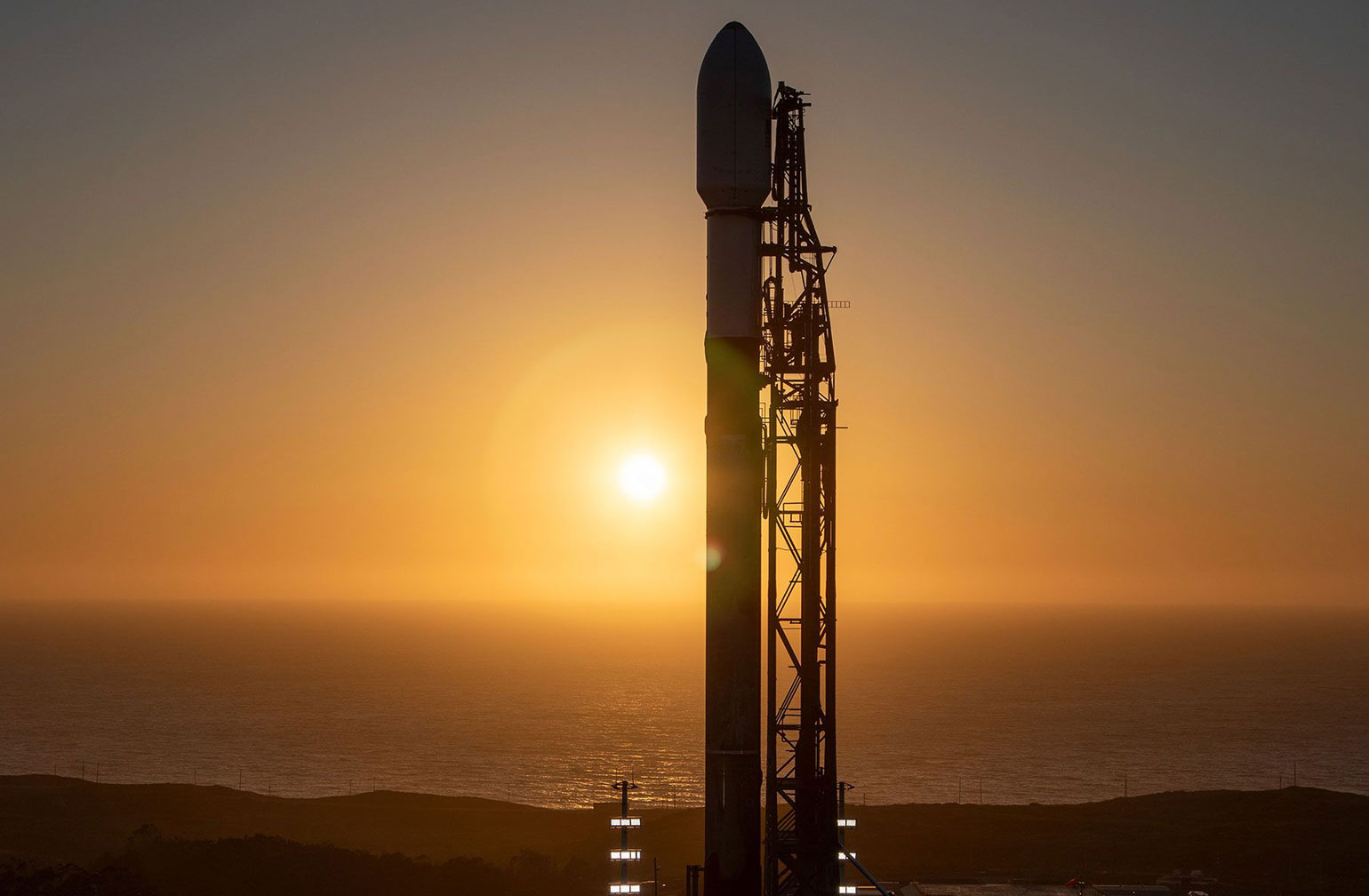
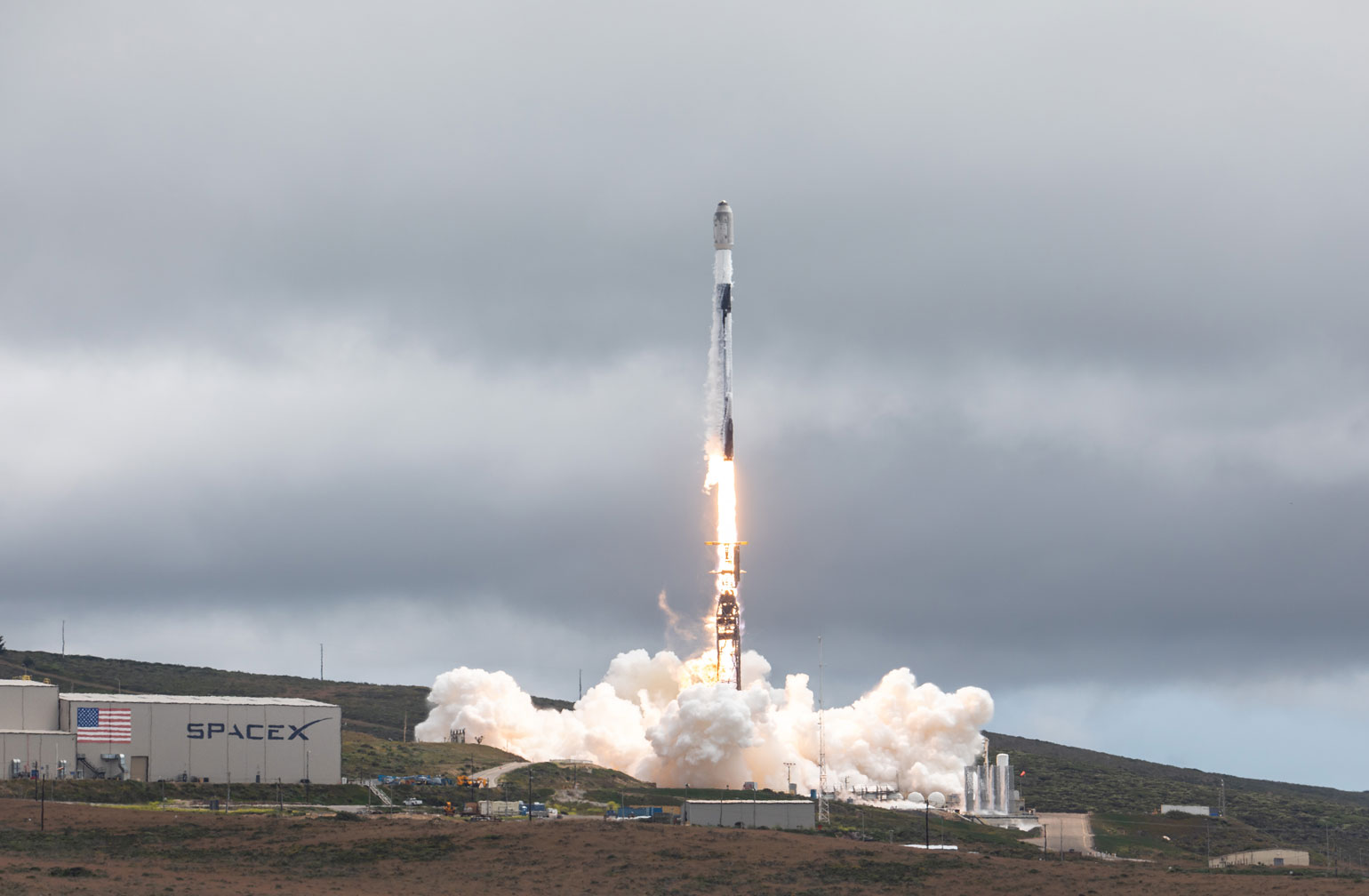
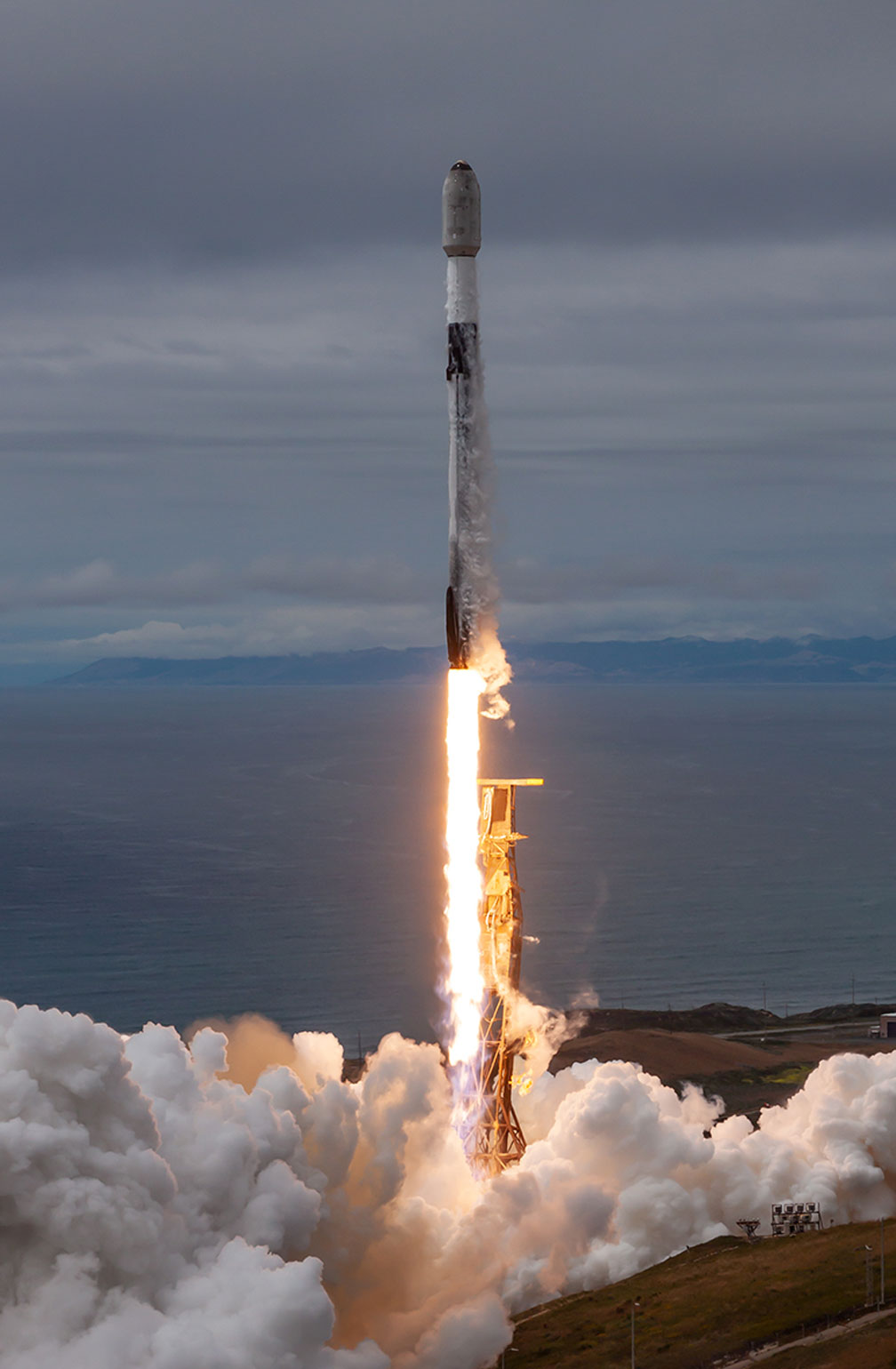
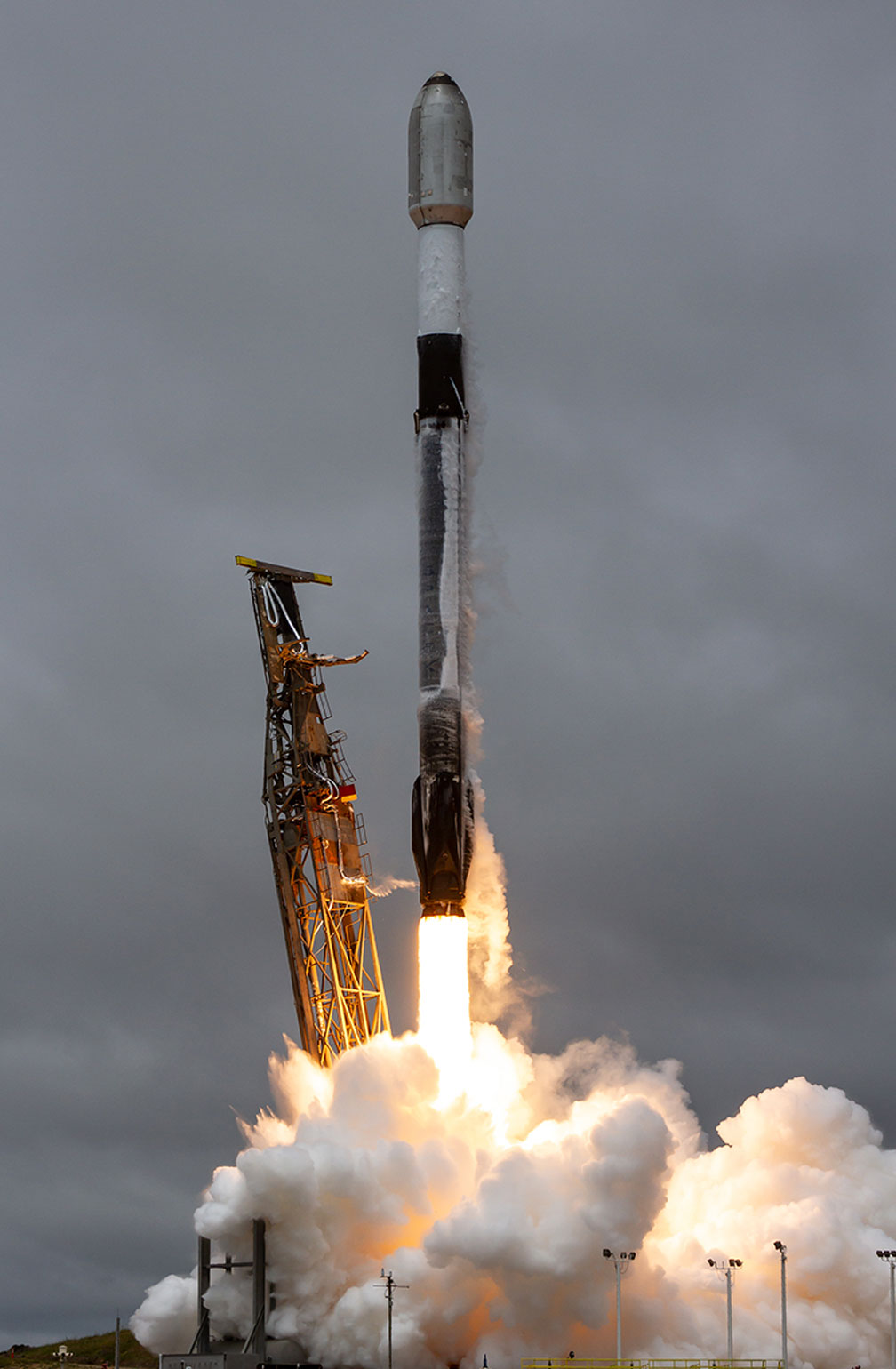
TRANSPORTER-8 MISSION
FALCON 9
12th June 2023
EIGHTH DEDICATED RIDESHARE MISSION WITH SPACEX
Mission
SpaceX’s SmallSat
Rideshare Program
Transporter - 8
Launch site
Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, USA
Launch Vehicle
Falcon 9
Launch Period
June 2023
32 satellites
Applications
-
Optical and SAR Earth Observation
Maritime Surveillance
ADS-B Tracking
Internet of Things
Technology Demonstration
Customers
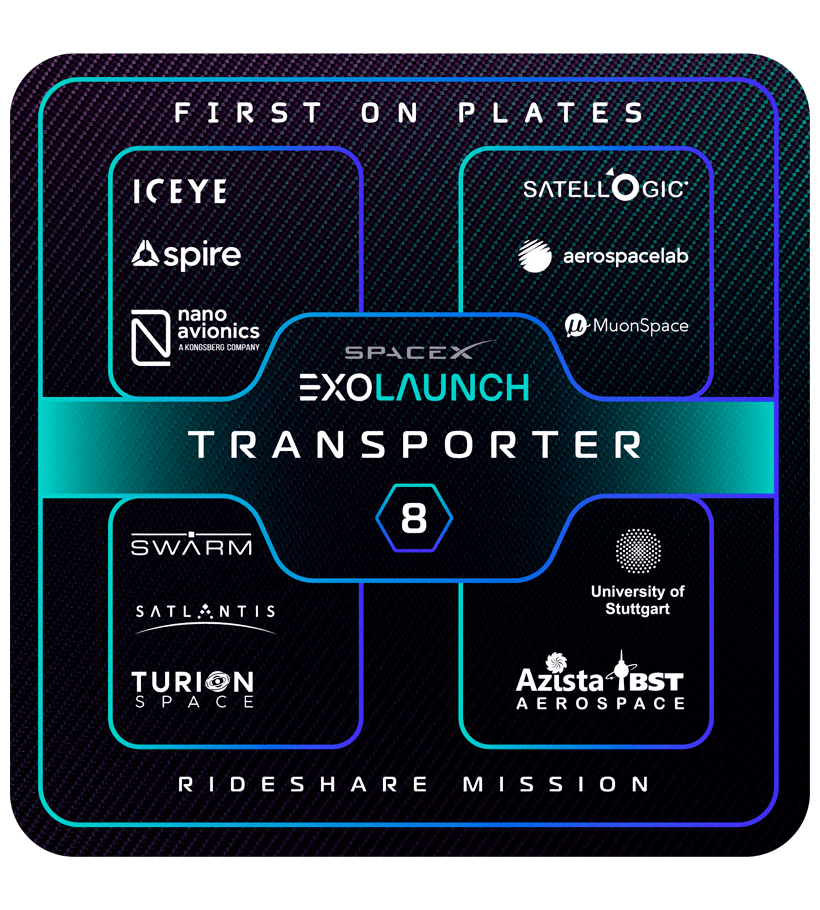
Spire, ICEYE, Satellogic, Kongsberg NanoAvionics, Satlantis, Swarm Technologies, TU Stuttgart,Aerospacelab, Muon Space, Turion Space and Azista BST Aerospace
Main payload
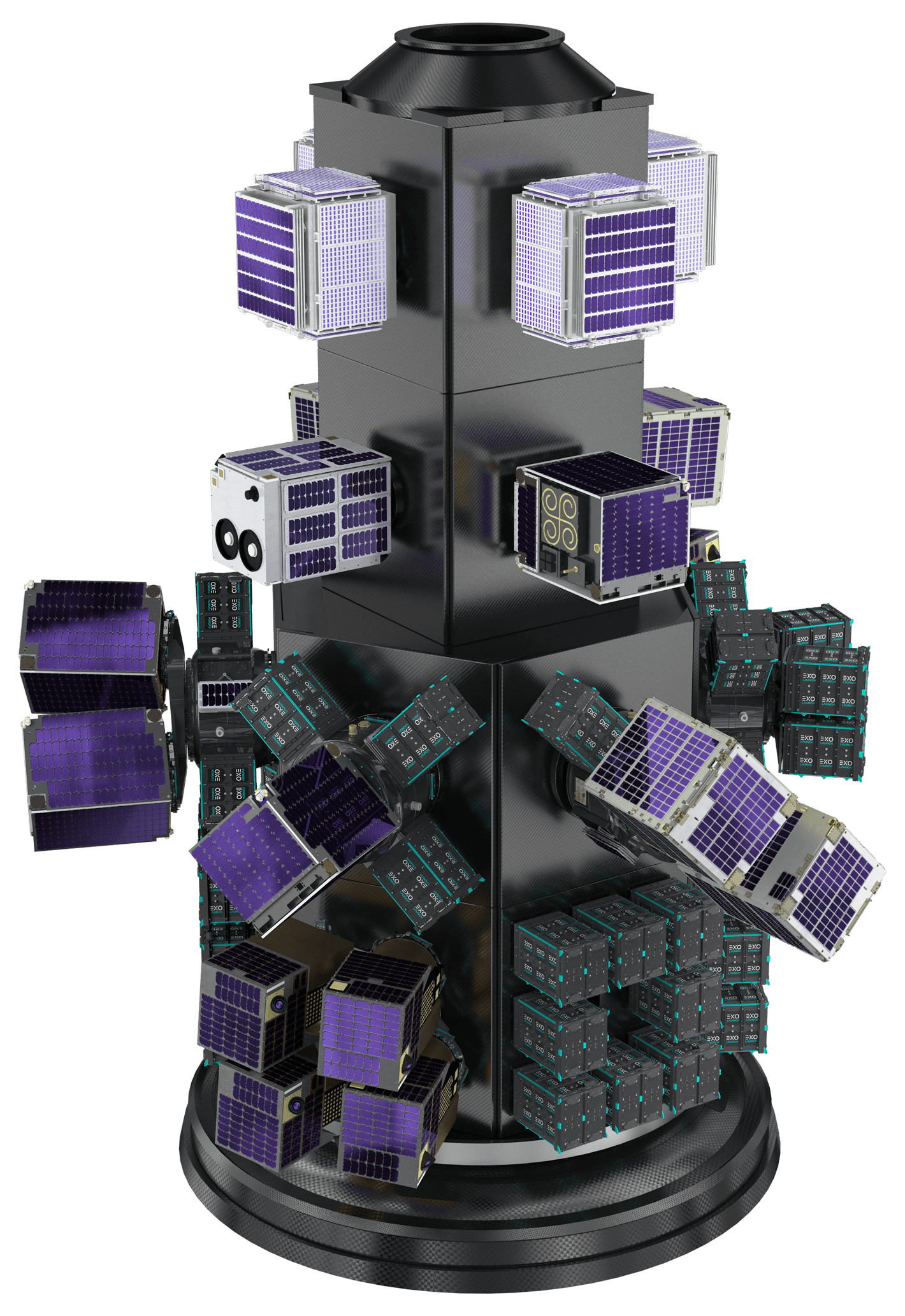
72 spacecraft, including CubeSats, MicroSats, a re-entry capsule, and orbital transfer vehicles
Launch site
Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, USA
Launch Period
June 2023
Applications
-
Optical and SAR Earth Observation
Maritime Surveillance
ADS-B Tracking
Internet of Things
Technology Demonstration
Main payload
72 spacecraft, including CubeSats, MicroSats, a re-entry capsule, and orbital transfer vehicles
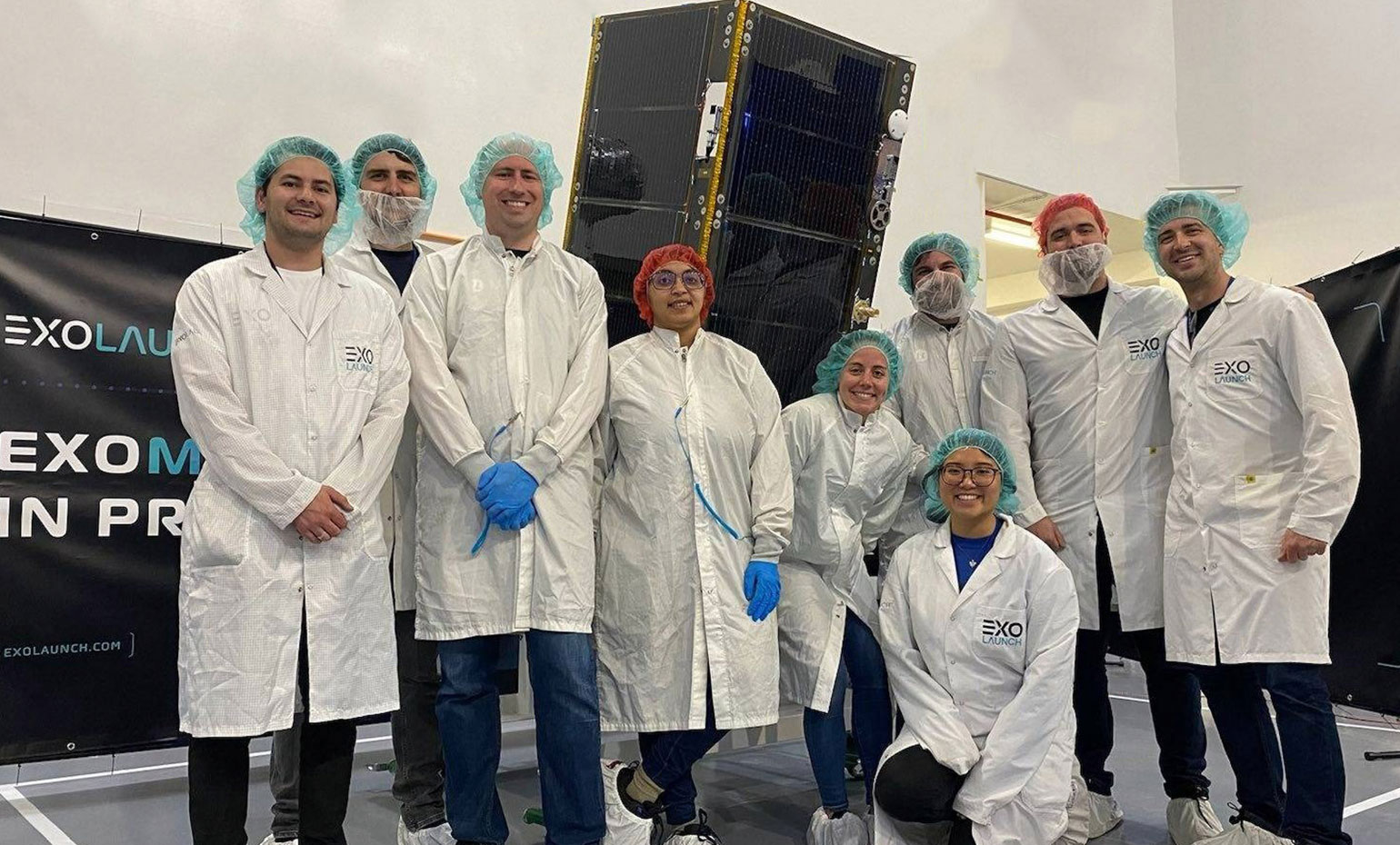
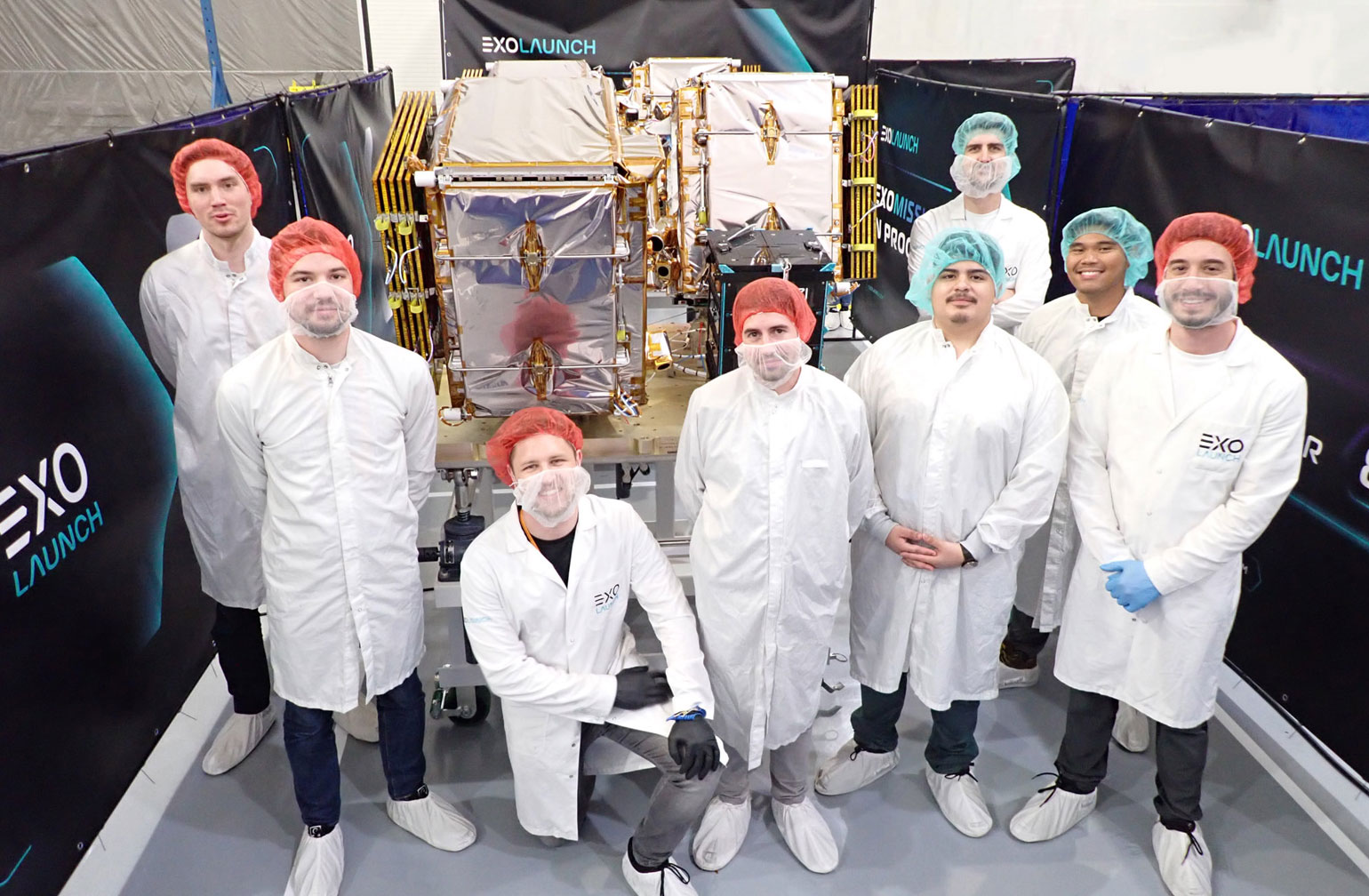
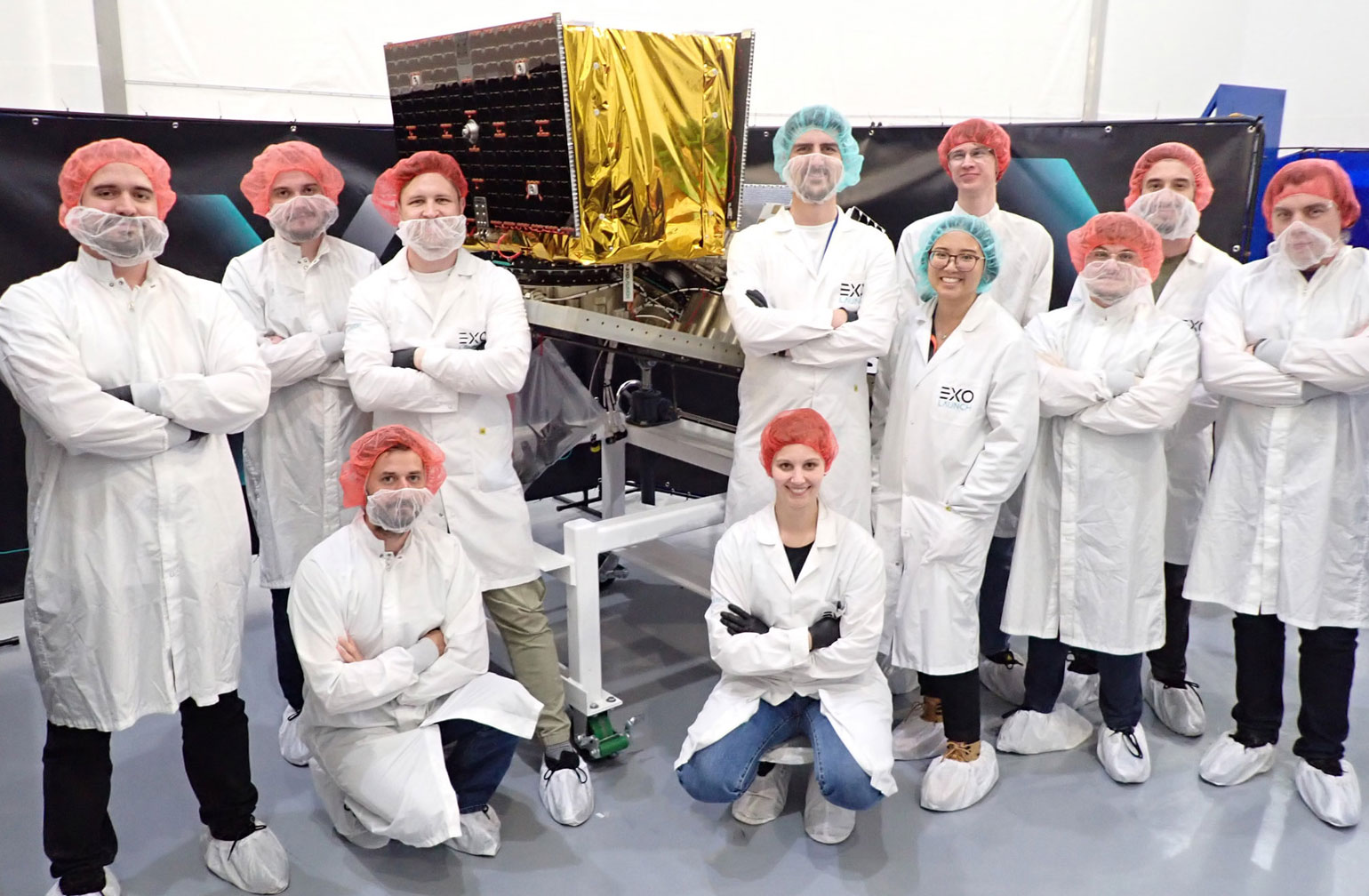
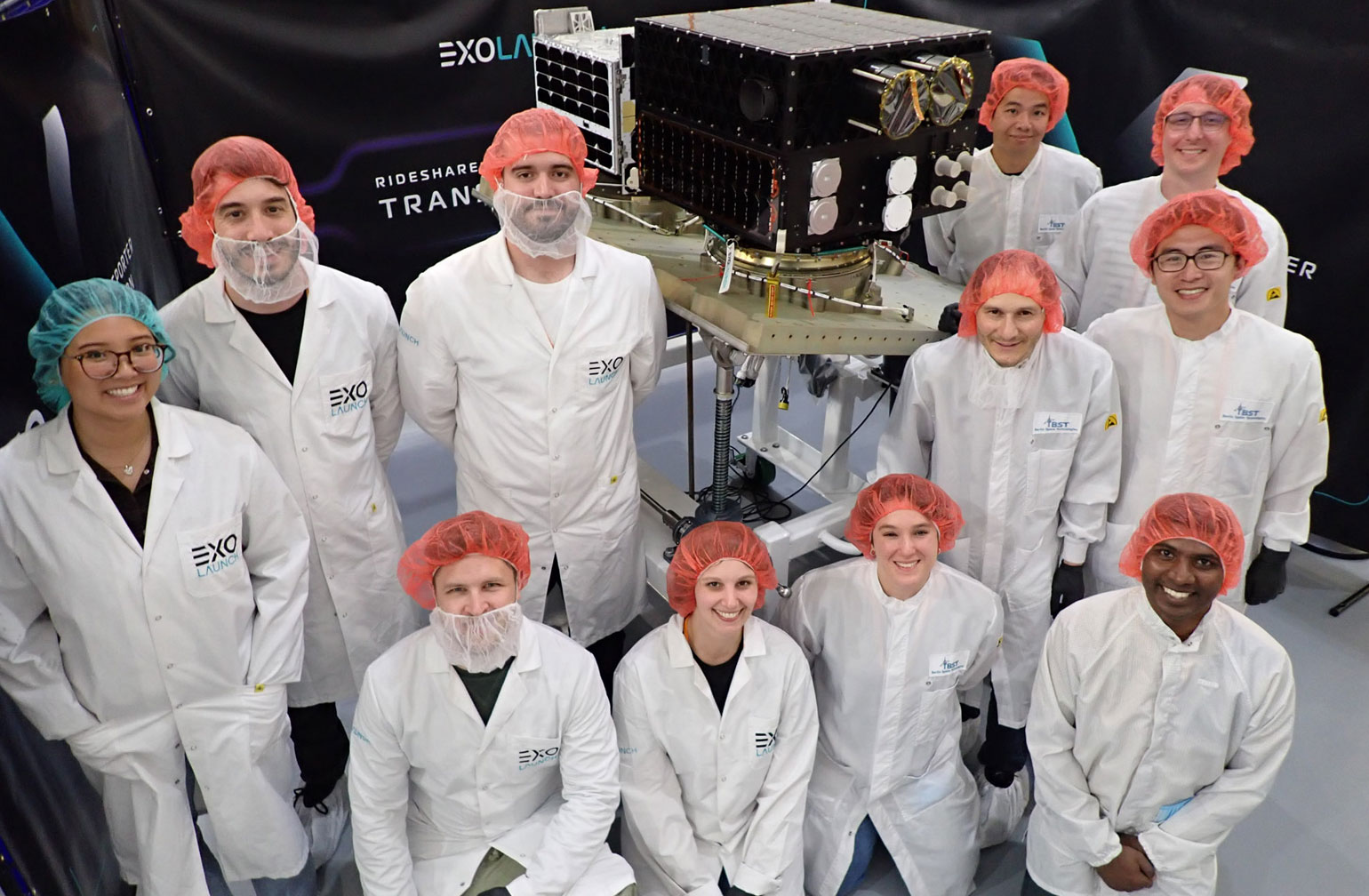
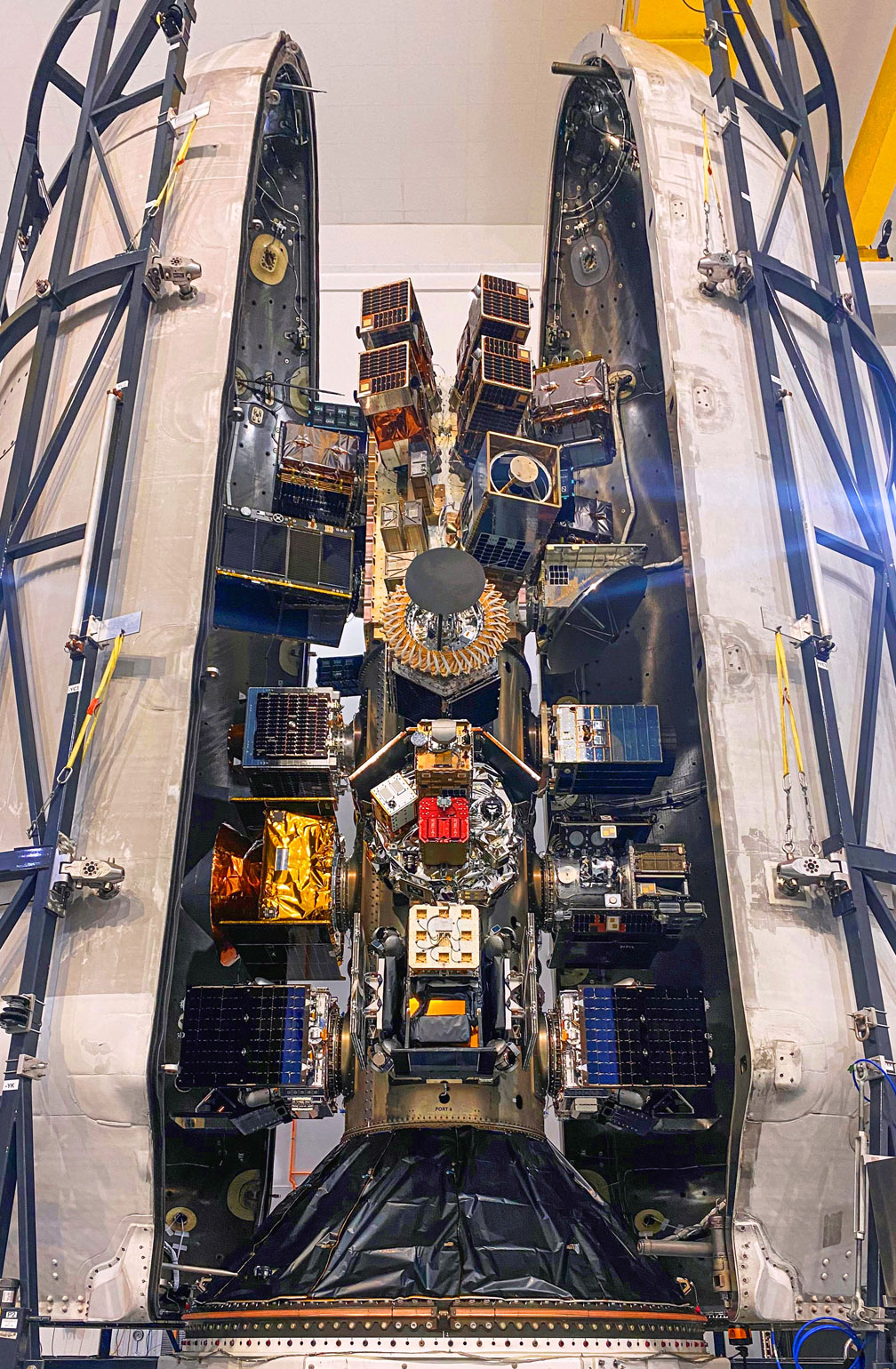
Mission overview
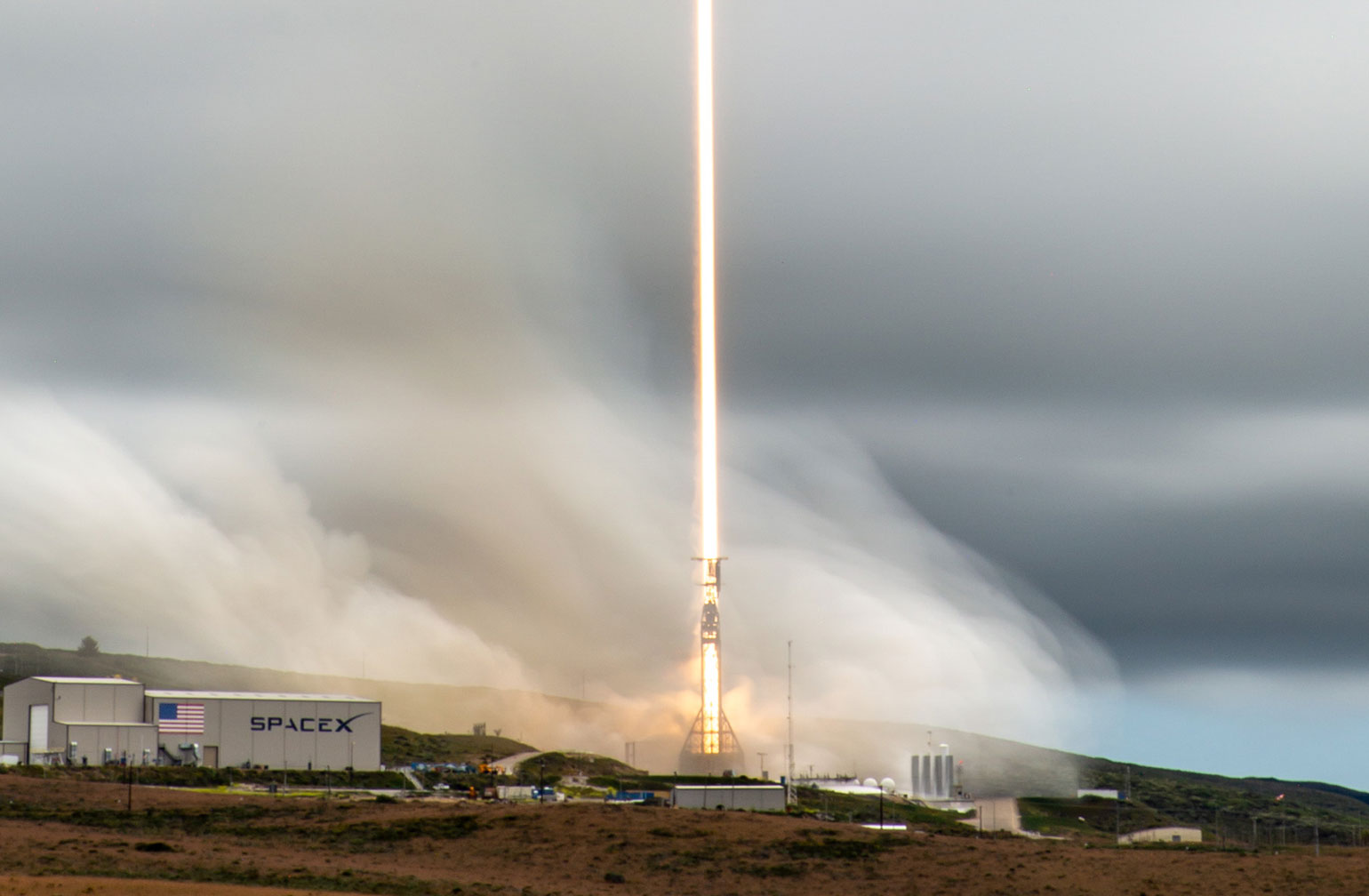
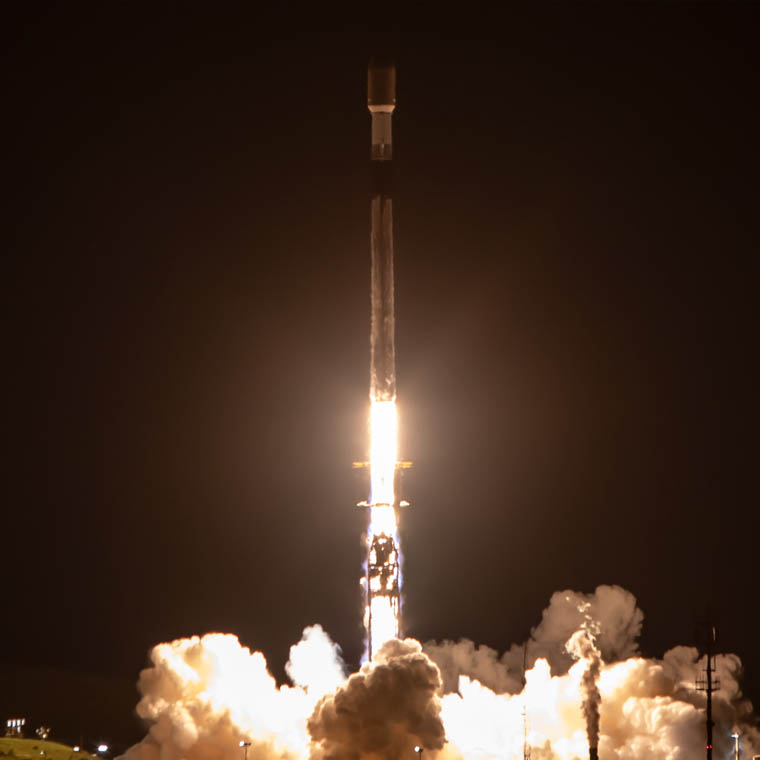
Transporter-8 saw Exolaunch surpass its 300th satellite launched. On this landmark mission, we deployed 32 satellites, bringing our flight heritage to a total of 323 satellites launched. This SpaceX dedicated rideshare mission lifted-off on a Falcon 9 on June 12, 2023 at 2:35pm PT from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, USA.
On its fourth mission this year, Exolaunch manifested a roster of 11 international customers, headlining long-standing customers Spire, ICEYE, Satellogic, Kongsberg NanoAvionics, Satlantis, Swarm Technologies, and TU Stuttgart. In addition, we were very pleased to welcome new customers Aerospacelab, Muon Space, Turion Space and Azista BST Aerospace. Our manifest on Transporter-8 features satellites intended for a diverse range of applications, including Earth observation, methane emissions monitoring, scientific experiments and more in a showcase of the Transporter program's broad appeal in the NewSpace sector.
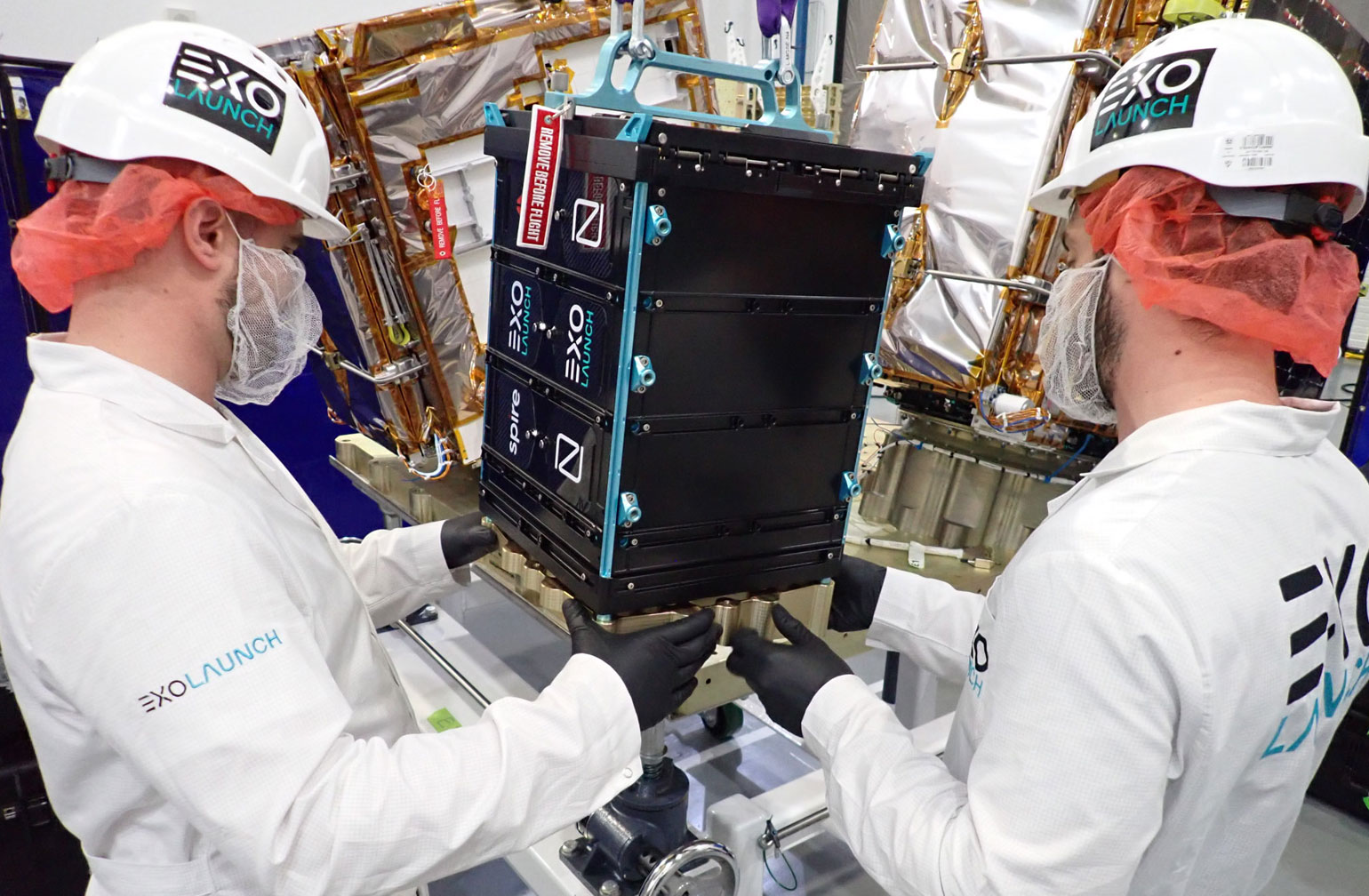
Transporter-8 marked a turning point in Falcon 9 rideshare missions as the first launch to utilize SpaceX’s modular Rideshare Plates to accommodate the mission’s payloads. Under our ongoing Multi-Launch Agreements with SpaceX, we provided our proprietary EXOpod / EXOpod Nova deployers and CarboNIX separation systems as well as end-to end mission management for all customers manifested on the new Rideshare Plates. In addition, we also provided Satellogic with deployment hardware, integration, and deployment services on an additional Rideshare Plate.
On Transporter-8, we leveraged our expertise from a dozen missions with SpaceX to execute seamless integrations for our customers with Falcon 9 and achieve flawless separations of all 12 microsatellites and 20 CubeSats into their target orbit. The success of Transporter-8 is a defining moment for our flight heritage, bolstering Exolaunch’s position as a trusted mission management and integration services provider and one of the first with flight-proven hardware on Rideshare Plates.
This achievement comes on the heels of a series of record-breaking missions executed by Exolaunch earlier this year. In April, we marked a historic industry-first by deploying the first 16U smallsat in GEO, shortly after breaking its internal record for the largest manifest with the Transporter-6 mission in January.
The pacing of Exolaunch missions continues to accelerate, having already outstripped the number of missions and satellites launched in 2022 in half the time. Exolaunch has augmented its capabilities to match a surge in demand for its products and services, including moving into brand new facilities in Berlin and growing its teams in Germany and the US.
FULL MISSION MANIFEST
-
SPIRE, LEMUR 2 NAZIYAH, LEMUR 2 AADAM-ALIYAH, LEMUR-2 EMBRIONOVIS
LEMUR 2 NAZIYAH, LEMUR 2 AADAM-ALIYAH and LEMUR-2 EMBRIONOVIS were deployed using EXOpod and EXOpod Nova deployers for Spire, a long-standing customer and a leading global provider of space-based data, analytics and space services delivered by one of the largest multipurpose satellite constellations in the world.
-
ICEYE, FOUR SATELLITES
Four satellites with a SAR payload were deployed using CarboNIX microsatellite separation systems for ICEYE, a long-running and valued customer. ICEYE delivers unmatched persistent monitoring capabilities for any location on earth. Owning the world's largest synthetic-aperture radar constellation, the company enables objective, data-driven decisions for its customers in sectors such as insurance, natural catastrophe response and recovery, security, maritime monitoring, and finance. ICEYE's data can be collected day or night, and even through cloud cover.
-
SATELLOGIC, NEWSAT-40 – NEWSAT-43
Satellogic's NewSat-40 through NewSat-43 were deployed using CarboNIX separation systems following launch aboard Spacex's Transporter-8 mission. Satellogic is a leader in sub-meter resolution Earth Observation (EO) data collection. The company designs, manufactures, and operates its own constellation of EO satellites. This mission deployed four additional NewSat Mark V satellites to the constellation, bringing the total number of spacecraft to 38 operational satellites.
-
SWARM TECHNOLOGIES, SPACEBEES 168 THROUGH 179
SpaceBEE 168 through 179 were deployed using an EXOpod Nova deployer for Swarm Technologies, a SpaceX company, and a returning customer. Swarm Technologies manufactures the world's smallest satellites, which operate in a constellation spread out like strings of pearls into a series of distributed sun-synchronous orbital planes. This configuration allows the satellites to provide reliable global network coverage.
-
UNIVERSITY OF STUTTGART, EIVE
EIVE was deployed using an EXOpod Nova deployer for the University of Stuttgart. EIVE hosts experimental transmitter and solar cell payloads that it will use to investigate transmission conditions in orbit and demonstrate the technology's frequency modulation capabilities. The University of Stuttgart's Institute of Space Systems is one of the largest in Europe and offers a wide range of teaching and research in numerous exciting topics in space technology and space applications. EIVE was produced in a consortium, with the Institute responsible for the design, integration, and testing of the satellite bus, as well as the operation of the satellite.
-
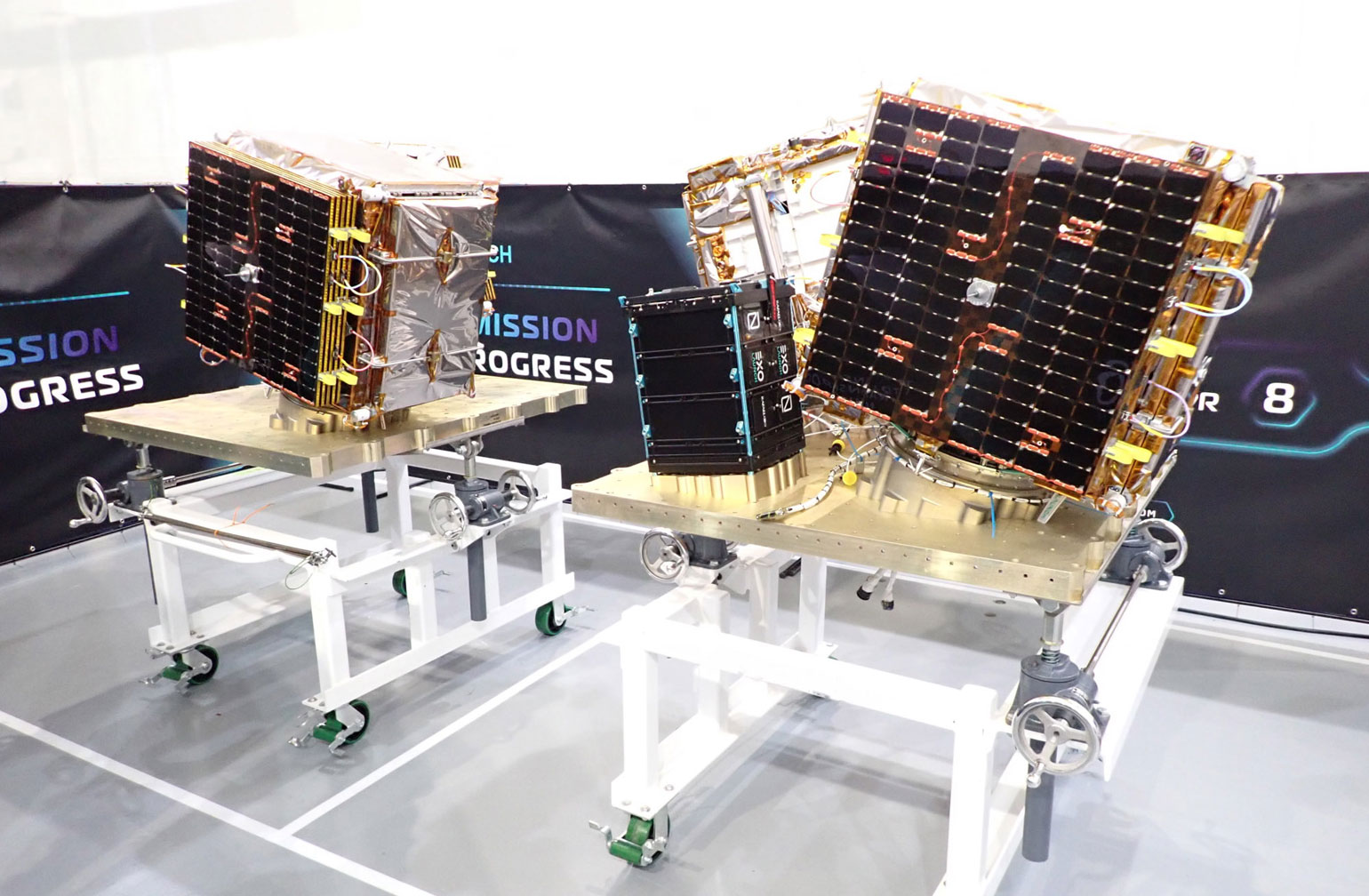
AEROSPACELAB, GRÉGOIRE
Grégoire was deployed using a CarboNIX separation system for Aerospacelab, a brand-new customer and fellow partner in the CASSINI Business Accelerator and YEESS. Founded in 2018, Aerospacelab is a fast-growing company specialized in designing, manufacturing and operating small satellite systems. Thanks to its versatile satellite platform, Aerospacelab provides international stakeholders with an access to space and geospatial intelligence, offering proprietary high-resolution satellite data and therefore facilitating improved decision-making based on information supported by reliable evidence. With a unique vertically integrated approach, the company is paving the road to an optimized and cost-efficient way to space. Headquartered in Mont-Saint-Guibert (Belgium), Aerospacelab has also offices in Switzerland and France with an overall headcount of over 200 employees.
-
MUON SPACE, MUSAT-1
MuSat-1 was deployed using a CarboNIX separation system for Muon Space, a new customer. MuSat-1 is a software-defined satellite optimized for remote sensing with powerful data bandwidth, flexible interfaces and a tightly integrated software stack. The satellite is designed to prove the Muon Space core technology stack that will serve as the backbone for its Constellation One network of small satellites. Founded in 2021, Muon Space is launching a new generation of sensors that monitor Earth's climate and ecosystems with unprecedented fidelity. From detecting and tracking wildfires and tsunamis to understanding global emissions, constellation scale sensing enables humanity to tackle global challenges.
-
TURION SPACE, DROID.001
DROID.001 was deployed using a CarboNIX separation system for Turion Space, a new start-up customer. DROID.001 is the first DROID satellite launched to provide Space Situational Awareness for Turion Space's customers. Turion Space builds spacecraft to remove orbital-debris and provide orbit-modification, inspection, and domain-awareness services to existing space assets. Turion Space believes the space debris problem must be solved to ensure a sustainable LEO economy and that it is the first technological step towards Asteroid resource extraction.
-
AZISTA BST AEROSPACE, AFR-1
AFR-1 was deployed using a CarboNIX separation system for Azista BST Aerospace, a new and deeply international customer. AFR-1 is an in-orbit demonstrator for Azista BST Aerospace's planned mass production microsatellite platform. Azista BST Aerospace (ABA) is an Indo-German Joint Venture with the vision of being the mass manufacturer of small satellites and a provider for mega-constellations. The Joint Venture enables the mastery of German heritage and design with Indian innovations and manufacturing prowess. ABA presently hosts the largest private satellite manufacturing facility in Asia.
-
SATLANTIS, GEI-SAT
GEI-SAT was deployed using an EXOpod Nova deployer for Satlantis, a returning customer. GEI-SAT features a high-resolution Earth observation payload to perform atmospheric CH4 measurements with high spatio-temporal resolution and simultaneous geolocation of source emitters, to be used for the monitorization and quantification of methane emissions in the Oil&Gas industry. SATLANTIS designs and manufactures Earth & Universe Observation payloads for Small Satellites, core of a unique set of electro-optical technologies. The company provides user-driven end-to-end small satellite solutions for diverse applications, including greenhouse gas detection, defence and intelligence, land monitoring, and much more.
featured customers
Ready to go
to space?
Let's chat. Get in touch and we'll be with you shortly.